Penile Implant Surgery
Penis Anatomy?
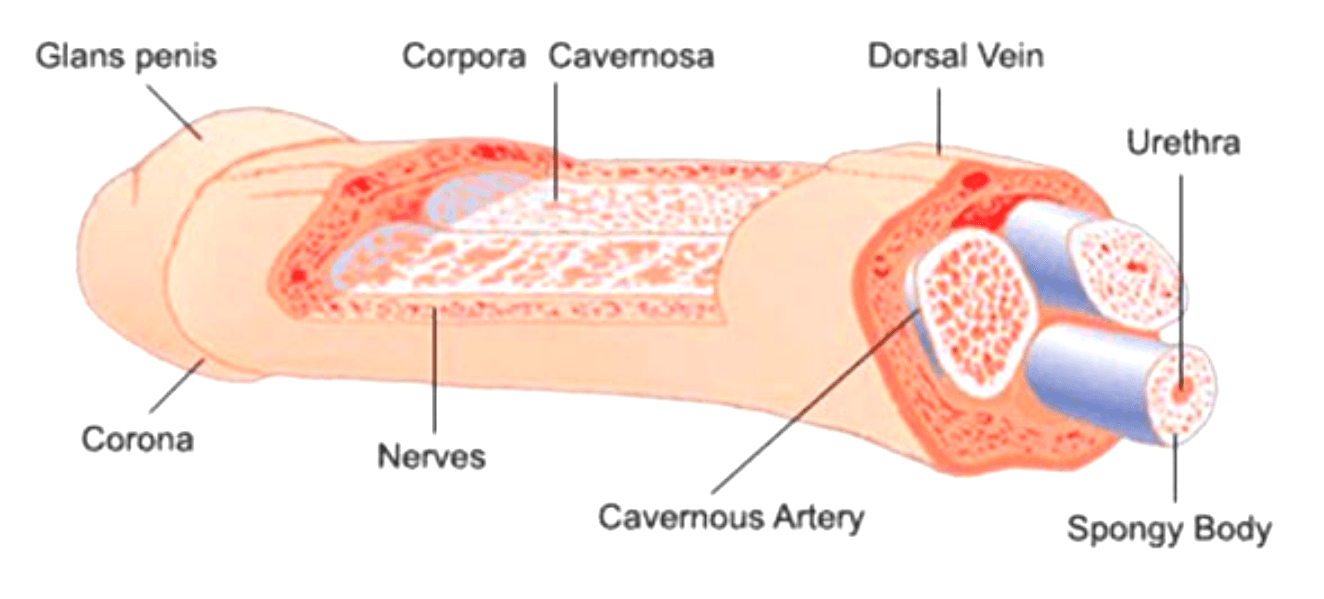
The penis contains two erection chambers called the corpora cavernosa, which run the length of the organ.
The corpora cavernosa is a spongy tissue that fills the chambers. The corpora cavernosa are surrounded by a membrane called the tunica albuginea.
The spongy tissue contains smooth muscles, fibrous tissues, spaces, veins, and arteries. The urethra, which is the channel for urine and ejaculate, runs along the underside of the corpora cavernosa and is surrounded by the corpus spongiosum.
What is a Penile Implant?
Penile implants are devices known as prostheses that can restore erection in many men with erection dysfunction. Implants are surgically inserted into the penis.
Penile implants require a surgical procedure and it is the most common surgery performed for treating erectile dysfunction.
Why Consider Penile Implant Surgery?
Where conservative and pharmacological treatment measures for erectile dysfunction have been unsuccessful or not satisfactory Penile implant surgery may be considered.
Penile implants can also be used to treat severe cases of a condition that causes scarring inside the penis, leading to curved, painful erections (Peyronie's disease).
Types of Penile Implants
Urological prosthetics include penile implants, artificial slings, sphincters and testicular prostheses.
There are two main types of implants are:
- Malleable implants
- Inflatable implant
Malleable Implants (two piece)
Malleable implants usually consist of paired rods which are inserted surgically into the corpora cavernosa. The user manually adjusts the position of the penis and, therefore, the rods.
Adjustment does not affect the width or length of the penis. These implants are best suited for patients who may have limited hand dexterity.
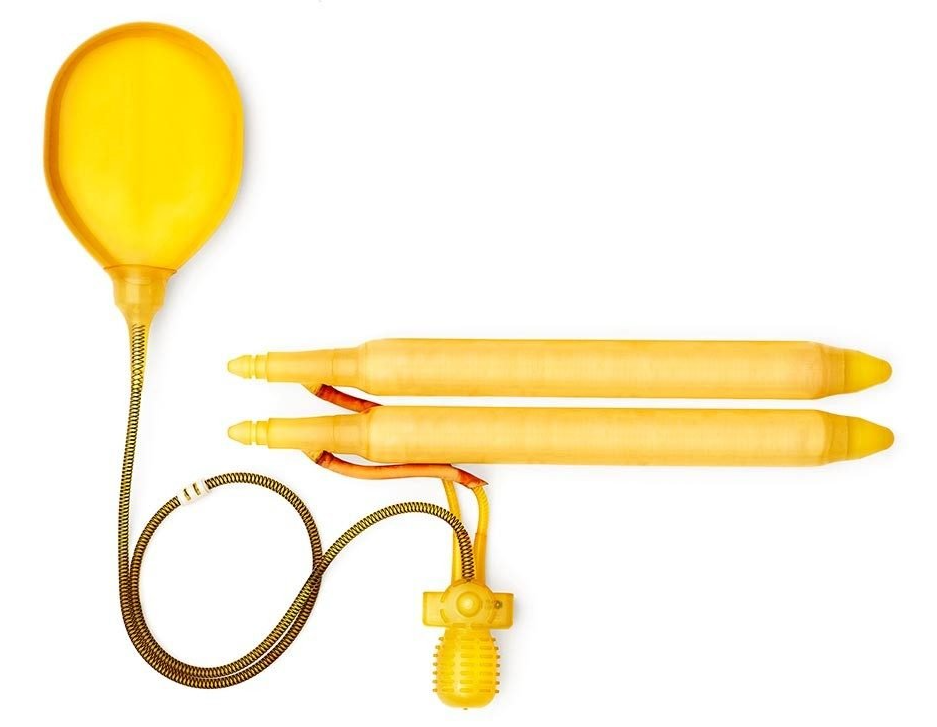
Inflatable Implants (three piece)
Inflatable implants consist of paired cylinders, which are surgically inserted inside the penis and can be expanded using pressurised fluid.
Tubes connect the cylinders to a fluid reservoir and a pump, which are also surgically implanted. The patient inflates the cylinders by pressing on the small pump, located under the skin in the scrotum.
As opposed to malleable implants, inflatable implants can expand the length and width of the penis. They also leave the penis in a more natural state when not inflated.
How is Penile Implant Surgery Performed
Dr Kim performs most of his penile implants using the MINT technique - "Minimally Invasive No Touch" approach.
- "Minimally Invasive" means that all components of the implant can be inserted via a 3-4 cm incision hidden in the pubic hair region. As the cut is so small, patients can be discharged the next day and post-surgery recovery is enhanced.
- "No Touch" means the implant does not touch the skin – which is a potential cause of infection. This MINT technique has a close to zero infection rate.
This video was made to teach other urologists how to perform penile implant surgery and therefore involves footage of real surgery which some people may find graphic.
Before Penile Implant Surgery
Before penile implant surgery you might also need to:
- Avoid certain medications. Dr Kim may recommend temporarily stopping aspirin and anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Arrange for a ride home, typically after an overnight stay.
- Nil By Mouth - Limit food and liquids after midnight prior to your surgery, or follow specific instructions from your anaesthetist.
During Penile Implant Surgery?
Penile implant surgery is done in a hospital under general anaesthetic and usually takes 60 - 90 minutes.
- The surgery site will also be shaved immediately before surgery to reduce the risk of infection
- A catheter may be used to collect urine at some point during surgery.
- The spongy tissue in the penis called the corpora cavernosa that would normally fill with blood during an erection is stretched.
- Dr Kim will choose the correct size implant and place the implant cylinders inside your penis. All sizes are customised to your exact body measurements.
- If Dr Kim is implanting a two-piece inflatable device, a pump and valve are placed inside the scrotum. For a three-piece device, Dr Kim will also implant a fluid reservoir under the abdominal wall through an internal incision.
- Once the device is in place, the incisions will be closed in multiple layers.
After Penile Implant Surgery
Dr Kim will give you antibiotics to help prevent infection and medications to ease the pain. Mild pain might persist for several weeks.
Most men can resume strenuous physical activity and sexual activity about four to six weeks after surgery. Dr Kim will provide specific instructions about when you can resume normal activities.
You will need to return to Dr Kim two weeks after surgery to have any stitches removed and for post-operative care
What to Expect After Penile Implant Surgery?
Penile implants allow men to get an erection, they don't increase sexual desire or sensation.
After a recovery period, Dr Kim might recommend fully inflating and deflating inflatable penile implants twice a day to give you practice using them and stretch the area surrounding the cylinders.
Although penile implants are the most invasive and least often chosen treatment for erectile dysfunction, most men report satisfaction with the devices. After 10-years penile implant devices have usage of between 60 and 80%.
Risks & Complications of Penile Implant Surgery
As with any surgery Penile Implant surgery carries risks. These include:
- Infection. As with any surgery, infection is possible but is higher given the nature of foreign body.
- Implant problems. New penile implant designs are reliable, but in rare cases, the implants might malfunction. Surgery is necessary to remove, repair or replace a broken implant.
- Internal erosion or adhesion. In some cases, an implant might stick to the skin inside the penis or wear away the skin from inside the penis. Rarely, an implant breaks through the skin. These problems are sometimes linked to an infection.